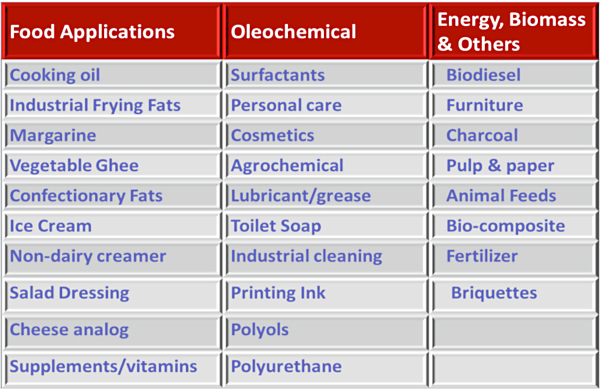
The four main traditional uses of palm oil in food products are for cooking/frying oil, shortenings, and margarine and confectionary fats. Palm oil is popularly used in both solid fat products as well as in the liquid cooking oil sector especially in industrial frying applications. It offers several technical characteristics desirable in food applications, such as resistance to oxidation, which contributes towards longer shelf life of end products. Palm oil is ideally suited for use as an ingredient in shortenings and margarines as it has 20 – 22% solid fat content (SFC) at 20°C, which helps in the formulation of fat products with a plastic range. It tends to crystallize in small beta-prime crystals, a property desirable for some applications, in particular table and industrial margarines. Palm oil also has other functional attributes that make it a valuable ingredient in food formulations. In many applications, palm oil can be combined with harder fractions such as palm stearin to produce products of the required consistency without hydrogenation. Common products made from palm oil and palm kernel oil, wholly or in blends with other oils include frying and cooking oils, shortenings, vegetable ghee or vanaspati, margarines and spreads, confectionery and non-dairy products.


The changing trends in lifestyles and demands for consumer products based on convenience and health considerations have led to other areas of applications for palm oil and its fractions. MPOB’s research and development (R&D) efforts have succeeded in formulating products to meet such demands, develop new niches, enter new markets and enhance of palm oil in foods include its use in emulsion-based powdered and consumer foods such as pourable margarine, mayonnaise, soup-mixes, imitation cheese and micro-encapsulated palm oil. Exciting products from new processes such as red palm oil or red palm olein have been introduced as healthy cooking and salad oils.
Palm oil products also find wide applications in the non-food sector, especially in the production of soaps and detergents, pharmaceutical products, cosmetics and oleochemical products. Soap production is one of the most important applications of oils and fats and the traditional raw materials used were tallow and coconut oil. Due to the similarity in their fatty acid compositions, palm and palm kernel oil offer good and competitive alternatives to tallow and coconut oil, respectively as raw material for soap making.
Fatty acids derived from the splitting process can be used directly in products like candle, cosmetics and in rubber processing. Derivatives of fatty acid include fatty esters (the most important of which is fatty acid methyl ester), fatty alcohols, fatty amines and fatty amides. Fatty esters are used in various industries such as biodiesel, textile, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, plastic and other applications. Though fatty alcohols as such find limited use, their derivatives; fatty sulphates are used extensively in the production of washing and cleaning products. Fatty amines are mainly used in the detergent industry as softening agents, in the mining industry as anti-caking agent, as biocides and in road building and other applications.

The changing trends in lifestyles and demands for consumer products based on convenience and health considerations have led to other areas of applications for palm oil and its fractions. MPOB’s research and development (R&D) efforts have succeeded in formulating products to meet such demands, develop new niches, enter new markets and enhance of palm oil in foods include its use in emulsion-based powdered and consumer foods such as pourable margarine, mayonnaise, soup-mixes, imitation cheese and micro-encapsulated palm oil. Exciting products from new processes such as red palm oil or red palm olein have been introduced as healthy cooking and salad oils.
Palm oil products also find wide applications in the non-food sector, especially in the production of soaps and detergents, pharmaceutical products, cosmetics and oleochemical products. Soap production is one of the most important applications of oils and fats and the traditional raw materials used were tallow and coconut oil. Due to the similarity in their fatty acid compositions, palm and palm kernel oil offer good and competitive alternatives to tallow and coconut oil, respectively as raw material for soap making.
Fatty acids derived from the splitting process can be used directly in products like candle, cosmetics and in rubber processing. Derivatives of fatty acid include fatty esters (the most important of which is fatty acid methyl ester), fatty alcohols, fatty amines and fatty amides. Fatty esters are used in various industries such as biodiesel, textile, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, plastic and other applications. Though fatty alcohols as such find limited use, their derivatives; fatty sulphates are used extensively in the production of washing and cleaning products. Fatty amines are mainly used in the detergent industry as softening agents, in the mining industry as anti-caking agent, as biocides and in road building and other applications.
Cosmetics
Besides the oil, there are huge amounts of oil palm wastes such as oil palm shells, mesocarp fibers and empty fruit bunches (from the mills), oil palm fronds and oil palm trunks (from the field during replanting) being generated by the industry. This oil palm biomass can be a raw material for many products such as medium density fiberboard (MDF), particleboard, pulp and paper, plastic composites, bio-compost and it is also used for bio-energy. The oil palm biomass can be a good alternative to replace wood in many applications.